Federal Employee Pay Raises Deconstructed
So, you're a federal employee and you're wondering about that sweet, sweet pay raise. Everyone likes more money, right? Well, the system isn't always straightforward. Let's dive into the murky waters of GS pay increases, particularly this idea of a "two-step" increase. Is it a myth? Is it a legend whispered in the halls of government buildings? Let's find out.
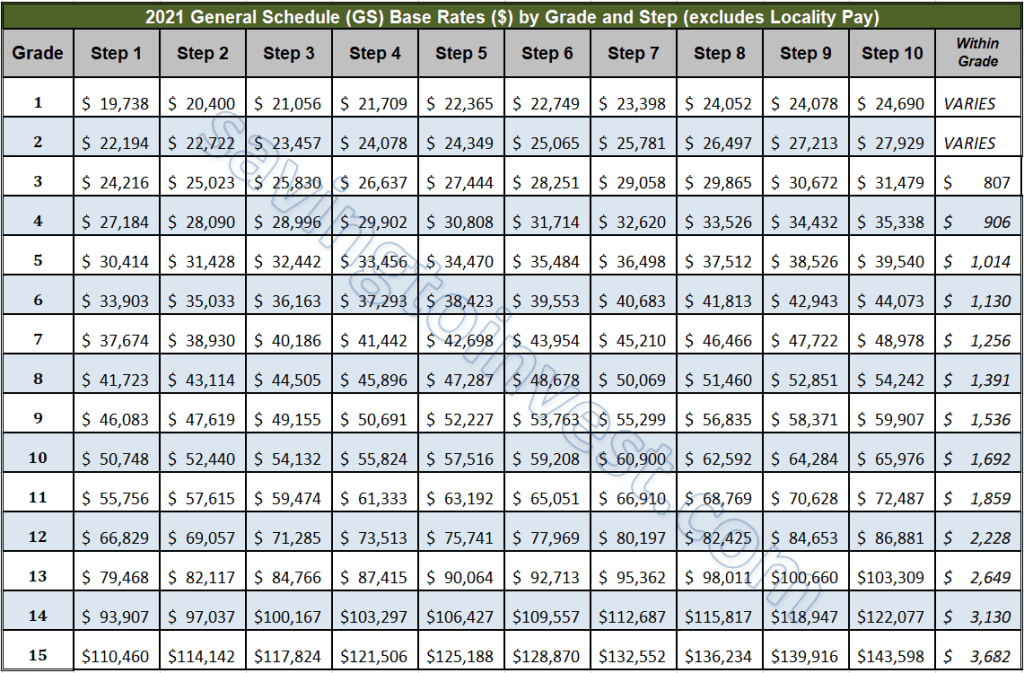
The GS pay scale is the backbone of the federal pay system. It's a structured framework that dictates how much federal employees earn based on their grade and step. A "step" represents a level within a grade, and typically, employees progress through steps based on time in service and performance. Now, this "two-step increase" concept isn't a formal policy, but it reflects the possibility of accelerated advancement within the GS system. It could happen through a promotion to a higher grade and a higher step within that grade, essentially skipping a few rungs on the ladder. This might occur due to exceptional performance, a special promotion program, or filling a critical need.
The General Schedule pay system has been around for decades, evolving to address economic changes and maintain competitive compensation for federal workers. Initially, the system was designed to provide fair and equitable pay across government agencies. The importance of a structured pay system like the GS scale lies in its transparency and consistency. However, it also faces challenges in keeping pace with private sector salaries and attracting top talent in specialized fields.
One of the main issues surrounding federal pay, including the possibility of two-step increases, is the perennial debate over pay comparability with the private sector. This leads to discussions about pay freezes, locality pay adjustments, and the impact on federal employee morale and recruitment. Furthermore, the complexities of the system can be confusing for employees to navigate, leading to questions about how advancements, promotions, and pay adjustments are calculated.
A "within-grade increase" (WIGI) is a periodic step increase earned by employees within their current grade based on satisfactory performance and time in service. Typically, employees advance one step at a time. The frequency of WIGIs varies depending on the step level. For example, progression between steps 1-3 might be faster than between steps 9-10. A faster progression resembling a "two-step" jump might occur with a promotion combined with a step increase within the new grade.
Let's break down a hypothetical scenario. Imagine a GS-9 employee at Step 5. A typical progression would be to Step 6 after a specified period. However, if this employee is promoted to GS-11 and placed at Step 2, that could be considered, in a sense, a "two-step" advancement, as it represents a significant jump in pay and grade level.
Benefits of accelerated advancement:
1. Increased Earning Potential: Faster progression means reaching higher salary levels more quickly.
2. Enhanced Morale and Motivation: Recognizing and rewarding high performance boosts employee morale.
3. Improved Recruitment and Retention: Competitive compensation packages attract and retain talent.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a "Two-Step" Advancement
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Faster salary growth | Can create pay disparities among colleagues |
| Increased motivation and morale | May not be accessible to all employees |
| Improved recruitment and retention | Can lead to feelings of inequity if not managed transparently |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a GS pay step increase? A step increase is a periodic pay raise within a specific GS grade.
2. How often do step increases occur? The frequency varies based on the step level.
3. How is a two-step increase possible? Typically through a promotion combined with a step increase within the new grade.
4. What factors influence GS pay? Grade level, step, locality pay, and special pay rates.
5. How can I find my locality pay rate? Check the OPM website.
6. How do I advance to a higher GS grade? Through promotion or competitive selection processes.
7. Where can I find more information about federal pay? Consult the OPM website and your agency's HR department.
8. What is the difference between a step increase and a grade increase? A step increase occurs within a grade, while a grade increase involves moving to a higher GS level.
Tips and Tricks: Understand your agency's promotion policies, document your achievements, network, and seek mentorship.
Understanding the intricacies of the GS pay system, including the nuances of "two-step" increases and within-grade increases, is crucial for federal employees. Navigating this system effectively can significantly impact your career trajectory and financial well-being. While a literal two-step increase is rare, accelerated advancement within the system is possible through promotions and strategic career planning. By staying informed, understanding your options, and actively managing your career progression, you can maximize your earning potential and achieve your professional goals within the federal government. This knowledge empowers federal employees to make informed decisions about their careers and advocate for their own advancement. Staying informed about changes in federal pay policies, including potential legislative actions affecting GS pay scales, is paramount for all federal workers. Take an active role in understanding your compensation and how it impacts your future. Don't just wait for things to happen – be proactive in your career development.
Unlock your brands potential with social media marketing video instruction
The allure of anime characters with split pink and black hair
The regressed demon lords kindness explored