Insect Respiration: How Bugs Breathe

Ever wonder how a tiny ant scurrying across the sidewalk gets the oxygen it needs to survive? Or how a buzzing bee fuels its flight through the air? The answer lies in a fascinating and often overlooked biological process: insect respiration. While it might seem like a simple question – do insects breathe air? – the mechanisms behind their respiration are surprisingly complex and utterly essential to their existence.
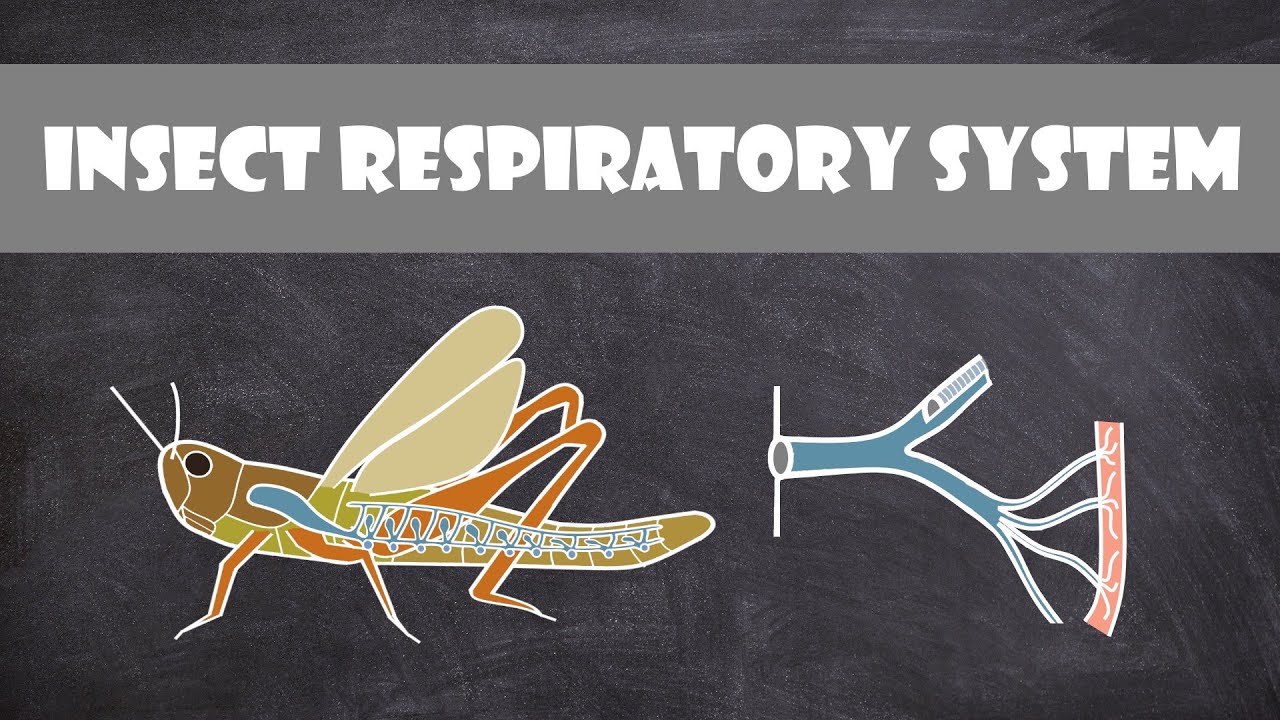
Unlike humans with lungs, insects utilize a unique system of tubes called tracheae to deliver oxygen directly to their tissues. This intricate network, spreading throughout their bodies like tiny branches, allows them to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide without the need for blood as a transport medium. It’s a remarkable adaptation that has allowed insects to thrive in virtually every terrestrial habitat on Earth.
The process of insect breathing begins with tiny openings on their exoskeleton called spiracles. These spiracles act as valves, regulating the flow of air into the tracheae. The tracheae then branch and subdivide into smaller tubes called tracheoles, which reach individual cells, ensuring that oxygen is delivered precisely where it's needed. This direct delivery system is incredibly efficient, allowing insects to maintain high metabolic rates and power their impressive feats of strength and endurance.
The evolution of this unique respiratory system is intrinsically linked to the success of insects as a group. Their ability to breathe air efficiently has allowed them to colonize diverse environments, from arid deserts to lush rainforests. Understanding how insects breathe provides crucial insights into their biology, ecology, and even their vulnerability to environmental changes.
The importance of insect respiration extends far beyond the individual insect. Insects play critical roles in pollination, decomposition, and nutrient cycling, making their survival essential for healthy ecosystems. Factors that interfere with insect respiration, such as air pollution or pesticides, can have cascading effects on the environment.
Insects do breathe air, although not in the same way as mammals. Their respiratory system doesn't rely on lungs but rather on a network of tracheae that delivers oxygen directly to their cells. For example, a grasshopper takes in air through spiracles located along its abdomen. These spiracles open and close, regulating the flow of air into the tracheal system.
One benefit of the insect respiratory system is its efficiency. The direct delivery of oxygen to cells allows for high metabolic rates, supporting the active lifestyles of many insects. Another benefit is its adaptability. Aquatic insects have evolved modifications to their spiracles and tracheae that allow them to extract oxygen from water or store air bubbles for underwater breathing.
Understanding how insects obtain oxygen is vital for pest control. Certain insecticides target the insect respiratory system, disrupting its function and leading to death. This knowledge can be used to develop more targeted and effective pest management strategies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Insect Respiratory System
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Efficient oxygen delivery | Vulnerable to desiccation (drying out) |
| Supports high metabolic rates | Limits body size |
| Adaptable to different environments | Susceptible to certain insecticides |
Five Real Examples of Insect Respiration
1. Grasshoppers use abdominal movements to pump air through their spiracles and tracheae.
2. Diving beetles carry air bubbles underwater, replenishing them at the surface.
3. Dragonfly nymphs extract oxygen from water using rectal gills.
4. Mosquito larvae breathe through a siphon located at the end of their abdomen.
5. Bees regulate their spiracles to control water loss during flight.
Frequently Asked Questions About Insect Respiration
1. Do all insects breathe air? Yes, with some adaptations for aquatic species.
2. How do insects breathe underwater? Some use gills, others carry air bubbles, and some have specialized spiracles.
3. What are spiracles? Small openings on the exoskeleton that regulate airflow.
4. What are tracheae? The tubes that carry air throughout the insect's body.
5. Why is insect respiration important? Essential for their survival and ecosystem roles.
6. How does insect respiration differ from human respiration? Insects don't have lungs and use a tracheal system.
7. Can air pollution affect insect respiration? Yes, it can disrupt the process and harm insects.
8. How can we learn more about insect respiration? Through books, websites, and entomological resources.
In conclusion, the way insects breathe air, through their intricate tracheal system, is a marvel of biological engineering. This efficient and adaptable respiratory system has allowed insects to flourish across the globe, playing essential roles in various ecosystems. From the tiny ant to the buzzing bee, the process of insect respiration is crucial for their survival and impacts the environment in countless ways. Understanding how insects breathe provides us with valuable insights into their biology, their importance, and the potential consequences of environmental changes. By learning more about insect respiration, we can better appreciate the intricate web of life and the vital role these small creatures play in it. Further research and exploration of this fascinating topic are crucial for advancing our understanding of insect biology and developing effective strategies for conservation and pest management.
Greenville craigslist car and truck deals navigating the marketplace
Luke combs brother death rumors debunked
Hack your health your way to wellness







/GettyImages-123521901-56eae07a3df78cb4b97bd6e4.jpg)