Unlocking the GS Pay Scale Secrets
Ever wonder how the salaries of those working for Uncle Sam are determined? It's not a random number generator, but a structured system called the General Schedule (GS) pay scale. This system, covering most white-collar federal employees, offers a transparent and predictable path for compensation, allowing employees to understand their earning potential and plan for their financial futures. Let's unravel the mysteries of this crucial element of federal employment.
The GS pay scale is the backbone of compensation for a vast majority of federal government civilian employees. Understanding it is crucial not just for those currently employed, but also for prospective federal workers. Knowing how the system works can significantly influence your career choices and financial planning. This system is more than just numbers; it's about fairness, transparency, and ensuring that the government attracts and retains a skilled workforce.
The history of the GS pay system can be traced back to the Classification Act of 1923, which aimed to standardize and professionalize the federal civil service. This Act laid the groundwork for a more systematic approach to compensation, moving away from arbitrary salaries and towards a structured system based on job responsibilities and performance. Over time, the GS pay scale has evolved to incorporate factors like locality pay adjustments, reflecting the varying cost of living across different regions of the country.
The GS pay scale is vital for a number of reasons. It promotes fairness and equity within the federal workforce by linking pay to the complexity and responsibility of the job. It also provides transparency, allowing employees to clearly understand how their salaries are determined and how they can advance. This transparency is essential for employee morale and for ensuring public trust in the fairness of the federal government's compensation practices.
One of the key issues surrounding the GS pay scale is the debate around its competitiveness with the private sector. Maintaining a competitive compensation structure is critical for attracting and retaining top talent. Another concern is ensuring that the locality pay adjustments accurately reflect the real cost of living differences across different areas, allowing federal employees to maintain a comparable standard of living regardless of their location.
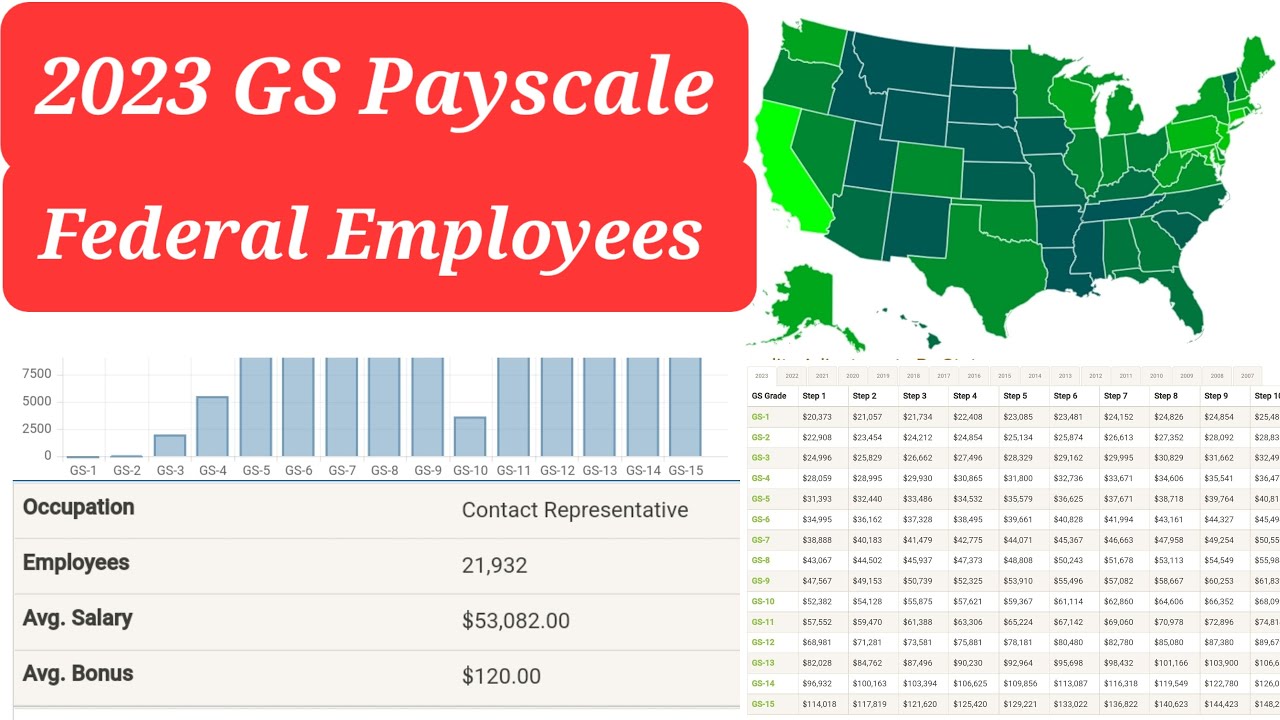
The GS pay scale comprises 15 grades, from GS-1 to GS-15, with each grade containing 10 steps. Your starting salary within a grade depends on your qualifications and experience. As you progress through the steps within your grade, your salary increases incrementally. Promotion to a higher grade typically results in a significant pay jump. Locality pay is an additional adjustment based on the cost of living in the area where you work, ensuring that your salary reflects local economic conditions.
Benefits of a structured pay scale include predictability, transparency, and motivation. Predictability allows for financial planning, transparency fosters trust, and the structured progression motivates employees to perform well and strive for advancement.
If you're considering a federal career, research the specific GS classification for your target role. Use online resources like the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) website to understand the pay ranges for your desired location. This allows you to align your career aspirations with your financial goals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Pay Scale
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency and Predictability | Can be less competitive than private sector in some fields |
| Job Security and Benefits | Salary progression can be slow |
| Clear Promotion Path | Limited negotiation power on starting salary |
Best practice is to research the locality pay adjustments for your desired area.
A real-world example is a GS-9 employee in Washington, D.C., earning more than a GS-9 employee in a lower-cost area due to locality pay.
One challenge is keeping the pay scale competitive, and a solution is regular reviews and adjustments.
FAQ: What is a GS step increase? Answer: A periodic within-grade salary increase based on satisfactory performance.
Tip: Use online calculators to estimate your potential salary based on grade and location.
The GS pay scale is the cornerstone of the federal government's compensation system. It offers a structured, transparent, and predictable approach to employee compensation. Understanding the nuances of the GS system, including grades, steps, and locality pay, empowers you to make informed career decisions. By taking the time to research and plan, you can navigate the system effectively and maximize your earning potential while serving the public. Remember that resources like the OPM website are readily available to help you understand the system and plan your career path. Take advantage of these resources to ensure your financial future within the federal government is as bright as possible. Taking charge of your financial future doesn't stop with understanding the pay scale; it extends to budgeting, saving, and investing wisely to build a secure and prosperous future.
Deku profile pictures a deep dive into the world of fan identity
Understanding medicaid fee for service reimbursement
Unveiling the world of a tree without roots manhwa polish edition